1.概述
对称密钥分组密码在数据加密中起着重要作用。这意味着加密和解密都使用相同的密钥。高级加密标准(AES)是一种广泛使用的对称密钥加密算法。
在本教程中,我们将学习如何在JDK中使用Java Cryptography Architecture(JCA)实现AES加密和解密。
2.AES算法
AES算法是一种迭代的对称密钥块密码,它支持128、192和256位的密钥(秘密密钥)来加密和解密128位块中的数据。下图显示了高级AES算法:
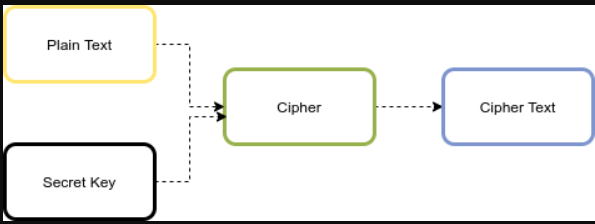
如果要加密的数据不满足128位的块大小要求,则必须对其进行填充。填充是将最后一个块填充为128位的过程。
3.AES变化
AES算法有六种操作模式:
- ECB(电子代码簿)
- CBC(密码块链接)
- CFB(密码反馈)
- OFB(输出反馈)
- CTR(计数器)
- GCM(伽罗瓦/计数器模式)
我们可以应用这种操作模式来加强加密算法的效果。此外,操作模式可以将分组密码转换为流密码。每种模式都有其长处和短处。让我们快速回顾每一个。
3.1. ECB
这种操作模式是最简单的。明文被划分为大小为128位的块。然后用相同的密钥和算法对每个块进行加密。因此,它对同一块产生相同的结果。这是该模式的主要弱点,不建议用于加密。它需要填充数据。
3.2.CBC
为了克服ECB的弱点,CBC模式使用初始化向量(IV)来增强加密。首先,CBC使用带有IV的明文块xor。然后将结果加密到密文块。在下一个块中,它使用加密结果与明文块异或,直到最后一个块。
在这种模式下,加密不能并行化,但解密可以并行化。它还需要填充数据。
3.3.CFB
此模式可以用作流密码。首先,它对IV进行加密,然后与明文块进行异或以获得密文。然后CFB对加密结果进行加密以异或明文。它需要IV。
在这种模式下,解密可以并行化,但加密不能并行化。
3.4.OFB
此模式可以用作流密码。首先对IV进行加密,然后利用加密结果对明文进行异或运算,得到密文。
它不需要填充数据,也不会受到嘈杂块的影响。
3.5.CTR
这种模式使用计数器的值作为IV。它与OFB非常相似,但每次都使用计数器而不是IV进行加密。
这种模式有两个优点,包括加密/解密并行化,并且一个块中的噪声不会影响其他块。
3.6.GCM
此模式是CTR模式的扩展。GCM受到了极大的关注,并得到了NIST的推荐。GCM模型输出密文和认证标签。与算法的其他操作模式相比,该模式的主要优点是其效率。
在本教程中,我们将使用AES/CCBC/PKCS5Padding算法,因为它在许多项目中被广泛使用。
3.7.加密后的数据大小
如前所述,AES具有128位或16字节的块大小。AES不会改变大小,密文大小等于明文大小。此外,在ECB和CBC模式中,我们应该使用类似PKCS 5的填充算法。因此,加密后的数据大小为:
ciphertext_size (bytes) = cleartext_size + (16 - (cleartext_size % 16))
为了用密文存储IV,我们需要再添加16个字节。
4.AES参数
在AES算法中,我们需要三个参数:输入数据、密钥和IV。IV在ECB模式中不使用。
4.1.输入数据
AES的输入数据可以是基于字符串、文件、对象和密码的。
4.2.密钥
AES中有两种生成密钥的方法:从随机数生成密钥,或者从给定的密码派生密钥。
在第一种方法中,密钥应该由加密安全(伪)随机数生成器(如SecureRandom类)生成。
为了生成密钥,我们可以使用KeyGenerator类。让我们定义一种生成大小为n(128、192和256)位的AES密钥的方法:
public static SecretKey generateKey(int n) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
keyGenerator.init(n);
SecretKey key = keyGenerator.generateKey();
return key;
}
在第二种方法中,可以使用类似PBKDF2的基于密码的密钥推导函数从给定密码推导AES密钥。我们还需要一个salt值来将密码转换为密钥。盐也是一个随机值。
我们可以将SecretKeyFactory类与PBKDF2WithHmacSHA256算法一起使用,从给定的密码生成密钥。
让我们定义一种方法,通过65536次迭代和256位的密钥长度从给定密码生成AES密钥:
public static SecretKey getKeyFromPassword(String password, String salt)
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidKeySpecException {
SecretKeyFactory factory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("PBKDF2WithHmacSHA256");
KeySpec spec = new PBEKeySpec(password.toCharArray(), salt.getBytes(), 65536, 256);
SecretKey secret = new SecretKeySpec(factory.generateSecret(spec)
.getEncoded(), "AES");
return secret;
}
4.3.初始化矢量(四)
IV是一个伪随机值,并且具有与加密的块相同的大小。我们可以使用SecureRandom类生成随机IV。
让我们定义一种生成IV的方法:
public static IvParameterSpec generateIv() {
byte[] iv = new byte[16];
new SecureRandom().nextBytes(iv);
return new IvParameterSpec(iv);
}
5.加密和解密
5.1.字符串
要实现输入字符串加密,我们首先需要根据上一节生成密钥和IV。下一步,我们使用getInstance()方法从Cipher类创建一个实例。
此外,我们使用init()方法配置了一个密码实例,该方法具有密钥IV和加密模式。最后,我们通过调用doFinal()方法来加密输入字符串。此方法获取输入的字节数,并以字节为单位返回密文:
public static String encrypt(String algorithm, String input, SecretKey key,
IvParameterSpec iv) throws NoSuchPaddingException, NoSuchAlgorithmException,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeyException,
BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(algorithm);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, iv);
byte[] cipherText = cipher.doFinal(input.getBytes());
return Base64.getEncoder()
.encodeToString(cipherText);
}
为了解密输入字符串,我们可以使用DECRYPT_MODE初始化我们的密码来解密内容:
public static String decrypt(String algorithm, String cipherText, SecretKey key,
IvParameterSpec iv) throws NoSuchPaddingException, NoSuchAlgorithmException,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeyException,
BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(algorithm);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, iv);
byte[] plainText = cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder()
.decode(cipherText));
return new String(plainText);
}
让我们编写一个用于加密和解密字符串输入的测试方法:
@Test
void givenString_whenEncrypt_thenSuccess()
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, IllegalBlockSizeException, InvalidKeyException,
BadPaddingException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, NoSuchPaddingException {
String input = "baeldung";
SecretKey key = AESUtil.generateKey(128);
IvParameterSpec ivParameterSpec = AESUtil.generateIv();
String algorithm = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
String cipherText = AESUtil.encrypt(algorithm, input, key, ivParameterSpec);
String plainText = AESUtil.decrypt(algorithm, cipherText, key, ivParameterSpec);
Assertions.assertEquals(input, plainText);
}
5.2. File
现在让我们使用AES算法对文件进行加密。步骤是相同的,但我们需要一些IO类来处理这些文件。让我们加密一个文本文件:
public static void encryptFile(String algorithm, SecretKey key, IvParameterSpec iv,
File inputFile, File outputFile) throws IOException, NoSuchPaddingException,
NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeyException,
BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(algorithm);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, iv);
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(inputFile);
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(outputFile);
byte[] buffer = new byte[64];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = inputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
byte[] output = cipher.update(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
if (output != null) {
outputStream.write(output);
}
}
byte[] outputBytes = cipher.doFinal();
if (outputBytes != null) {
outputStream.write(outputBytes);
}
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
请注意,不建议尝试将整个文件读取到内存中,尤其是在文件很大的情况下。相反,我们一次加密一个缓冲区。
对于解密文件,我们使用类似的步骤,并使用DECRYPT_MODE初始化密码,如前所述。
再次,让我们定义一个用于加密和解密文本文件的测试方法。在这种方法中,我们从测试资源目录中读取baeldung.txt文件,将其加密到一个名为baeldung.encrypted的文件中,然后将该文件解密到一个新文件中:
@Test
void givenFile_whenEncrypt_thenSuccess()
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, IOException, IllegalBlockSizeException,
InvalidKeyException, BadPaddingException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException,
NoSuchPaddingException {
SecretKey key = AESUtil.generateKey(128);
String algorithm = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
IvParameterSpec ivParameterSpec = AESUtil.generateIv();
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("inputFile/baeldung.txt");
File inputFile = resource.getFile();
File encryptedFile = new File("classpath:baeldung.encrypted");
File decryptedFile = new File("document.decrypted");
AESUtil.encryptFile(algorithm, key, ivParameterSpec, inputFile, encryptedFile);
AESUtil.decryptFile(
algorithm, key, ivParameterSpec, encryptedFile, decryptedFile);
assertThat(inputFile).hasSameTextualContentAs(decryptedFile);
}
5.3.基于密码
我们可以使用从给定密码派生的密钥进行AES加密和解密。
为了生成密钥,我们使用getKeyFromPassword()方法。加密和解密步骤与字符串输入部分中所示的步骤相同。然后,我们可以使用实例化的密码和提供的密钥来执行加密。
让我们写一个测试方法:
@Test
void givenPassword_whenEncrypt_thenSuccess()
throws InvalidKeySpecException, NoSuchAlgorithmException,
IllegalBlockSizeException, InvalidKeyException, BadPaddingException,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, NoSuchPaddingException {
String plainText = "www.baeldung.com";
String password = "baeldung";
String salt = "12345678";
IvParameterSpec ivParameterSpec = AESUtil.generateIv();
SecretKey key = AESUtil.getKeyFromPassword(password,salt);
String cipherText = AESUtil.encryptPasswordBased(plainText, key, ivParameterSpec);
String decryptedCipherText = AESUtil.decryptPasswordBased(
cipherText, key, ivParameterSpec);
Assertions.assertEquals(plainText, decryptedCipherText);
}
5.4.对象
为了加密Java对象,我们需要使用SealedObject类。对象应该是可序列化的。让我们从定义学生类开始:
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
// standard setters and getters
}
接下来,让我们加密Student对象:
public static SealedObject encryptObject(String algorithm, Serializable object,
SecretKey key, IvParameterSpec iv) throws NoSuchPaddingException,
NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException,
InvalidKeyException, IOException, IllegalBlockSizeException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(algorithm);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, iv);
SealedObject sealedObject = new SealedObject(object, cipher);
return sealedObject;
}
加密的对象稍后可以使用正确的密码进行解密:
public static Serializable decryptObject(String algorithm, SealedObject sealedObject,
SecretKey key, IvParameterSpec iv) throws NoSuchPaddingException,
NoSuchAlgorithmException, InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, InvalidKeyException,
ClassNotFoundException, BadPaddingException, IllegalBlockSizeException,
IOException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(algorithm);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, iv);
Serializable unsealObject = (Serializable) sealedObject.getObject(cipher);
return unsealObject;
}
现在让我们编写一个测试用例:
@Test
void givenObject_whenEncrypt_thenSuccess()
throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, IllegalBlockSizeException, InvalidKeyException,
InvalidAlgorithmParameterException, NoSuchPaddingException, IOException,
BadPaddingException, ClassNotFoundException {
Student student = new Student("Baeldung", 20);
SecretKey key = AESUtil.generateKey(128);
IvParameterSpec ivParameterSpec = AESUtil.generateIv();
String algorithm = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
SealedObject sealedObject = AESUtil.encryptObject(
algorithm, student, key, ivParameterSpec);
Student object = (Student) AESUtil.decryptObject(
algorithm, sealedObject, key, ivParameterSpec);
assertThat(student).isEqualToComparingFieldByField(object);
}
6.结论
在本文中,我们学习了如何在Java中使用AES算法对字符串、文件、对象和基于密码的数据等输入数据进行加密和解密。此外,我们还讨论了AES的变化和加密后数据的大小。
和往常一样,文章的完整源代码是可用的
- 登录 发表评论